Gastroenteritis Demystified: Everything You Need to Know
Few common ailments are more widespread and disruptive than gastroenteritis. Sometimes known as the stomach flu or stomach virus, can hit unexpectedly, causing discomfort and difficulty. But what is gastroenteritis, and how can we effectively manage its symptoms and treatments? Join us as we explore the realm of gastroenteritis and shed light on this frequently misunderstood ailment.
What is Gastroenteritis
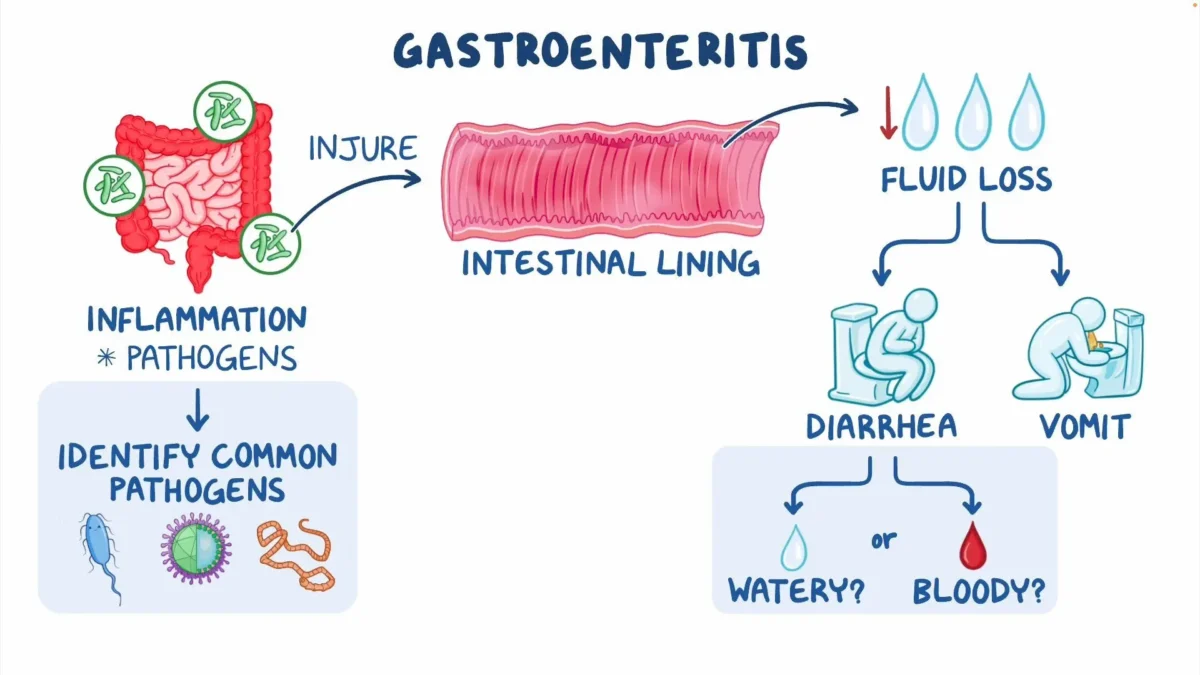
It is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and, in some cases, fever. While gastroenteritis is sometimes referred to as the stomach flu, it is vital to distinguish it from influenza, which predominantly affects the respiratory system.
Causes of Stomach Bug
The most prevalent cause of gastroenteritis is viral illness, with norovirus and rotavirus being the primary culprits, particularly in youngsters. Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella, and Campylobacter, can also cause gastroenteritis, which is often the result of contaminated food or drink. Furthermore, parasite illnesses like Giardia lamblia can cause gastroenteritis, though they are less common in wealthy countries.
Symptoms of Gastroenteritis
Stomach bug presents a constellation of symptoms that can vary in severity and duration. The hallmark symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea, often watery or loose stools
- Abdominal cramps or pain
- Fever (in some cases)
These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by dehydration, especially in cases involving significant fluid loss through vomiting and diarrhea.
Treatment and Management
While gastroenteritis is typically self-limiting and resolves on its own within a few days, supportive care is crucial to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. The following strategies can help manage gastroenteritis effectively:
- Fluid Replacement: Rehydration is critical in the treatment of gastroenteritis, especially in instances including vomiting and diarrhea. Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) with electrolytes can assist restore fluid and electrolyte balance. In severe cases, intravenous fluids may be required to avoid dehydration.
- Dietary modifications: During the acute phase of gastroenteritis, it is recommended to eat bland, readily digestible foods such rice, bananas, applesauce, and toast (the BRAT diet). Avoiding spicy, fatty, and high-fiber foods can assist to alleviate stomach distress.
- Medications: Some over-the-counter drugs, such as antiemetics (for nausea and vomiting) and antidiarrheals, may provide symptomatic relief. However, these medications should only be used with caution and under medical supervision, particularly in youngsters and the elderly.
- Rest and Recovery: Adequate rest is required for the body’s recovery from stomach bug. Avoiding strenuous activity and getting enough sleep helps boost the immune system and facilitate healing.
- Prevention: Good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, particularly before eating and after using the restroom, can help prevent the spread of gastroenteritis-causing germs. Furthermore, ensuring food safety and avoiding contaminated food or water might help lower the risk of infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
While most episodes of gastroenteritis may be treated at home with supportive care, certain warning signs require immediate medical intervention. This includes:
Signs of dehydration include
- Extreme thirst, dry mouth, reduced urine, and lightheadedness.
- Persistent high fever (over 102°F/39°C)
- Bloody stools or significant abdominal ache.
Symptoms of severe dehydration in newborns or young children, such as sunken fontanelle (soft spot), drowsiness, or fussiness
If you or a loved one exhibits any of these symptoms, it is critical to seek medical attention immediately.
Gastroenteritis, while unpleasant, is a common and typically self-limiting illness. We can confidently traverse this stomach illness after we understand its causes, symptoms, and suitable management options. Remember, when in doubt, put on your whitecoat of knowledge and seek advice from healthcare specialists to guarantee best care and recovery.